Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a ruggedized digital computer used for industrial automation. PLCs are designed to withstand harsh environments and control processes by monitoring inputs and controlling outputs based on user-defined logic. They are programmed using specialized software and a programming language like ladder logic or function block diagram. PLCs are integral to factory automation, controlling machinery, assembly lines, and processes in industries ranging from manufacturing to transportation. They offer flexibility, reliability, and real-time control, making them essential components in modern industrial automation systems.

Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) is a centralized system that monitors and controls industrial processes, infrastructure, and facilities. SCADA systems gather real-time data from sensors and devices, allowing operators to visualize, analyze, and manage processes remotely. They integrate with PLCs and other control devices to regulate and automate operations across various industries, including energy, water treatment, transportation, and manufacturing. SCADA systems provide a graphical interface for operators to monitor processes, receive alarms, and intervene when necessary. They enhance operational efficiency, improve safety, and facilitate data-driven decision-making in complex industrial environments.
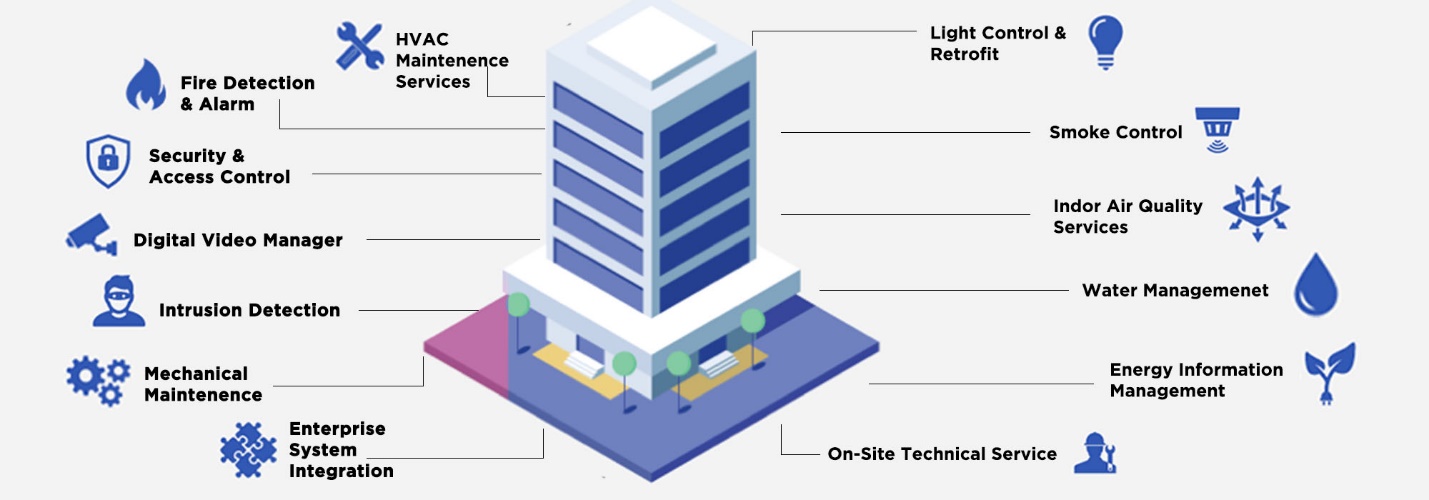
A Building Management System (BMS) is a computer-based control system that monitors and manages a building's mechanical and electrical equipment, such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, and security systems. BMS collects data from sensors and devices throughout the building, allowing operators to optimize energy usage, maintain occupant comfort, and ensure efficient operation of building systems. Through a centralized interface, users can monitor and control various parameters, receive alerts for faults or anomalies, and schedule maintenance tasks. BMS plays a crucial role in enhancing building performance, reducing energy consumption, and improving overall operational efficiency and sustainability.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, enabling them to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding. AI technologies include machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics. AI systems analyze large datasets, recognize patterns, and make predictions or decisions autonomously. They are used in various fields, including healthcare, finance, transportation, education, and entertainment, to automate processes, enhance decision-making, improve productivity, and develop innovative solutions. AI continues to evolve rapidly, shaping the future of technology and transforming industries worldwide.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices, sensors, machines, and systems within industrial environments that communicate and share data over the internet. IIoT leverages technologies like sensors, cloud computing, edge computing, and data analytics to collect, monitor, analyze, and optimize industrial processes in real-time. It enables remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, process optimization, and enhanced decision-making, leading to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved safety in industries such as manufacturing, energy, transportation, and utilities. IIoT plays a pivotal role in the digital transformation of industrial operations, driving innovation and competitiveness in the global market.








